What is Business Process Management?
Business Process Management is a way to understand, control, and improve an organization’s processes to deliver value to stakeholders. Moreover, this is a key concept of Six Sigma. You want to use systematic methods to create the best possible business results instead of improving local components.
Most organizations work as functional groups such as design, production, R&D, sales and marketing, production, quality, information technology, etc. In short, all these functional groups aim to produce the product or service for the customers. However, often these functional groups work in silos. For that reason, business process management helps manage the entire process, including determining the responsibilities of functional groups.
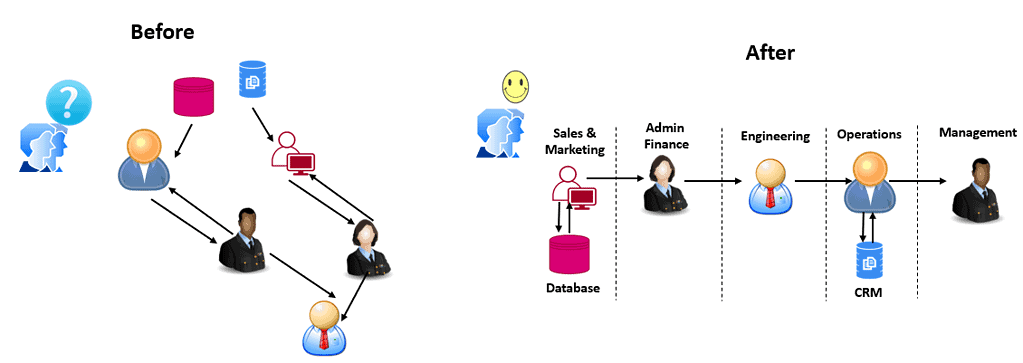
Business process management ensures that all the processes operate smoothly without delays or lack of resources. In other words, the basic aim of a business system is to ensure that the processes, products, and services are subjected to continuous improvement. A business system must explicitly provide scope for collecting and analyzing data from processes and other reliable sources to ensure continuous improvement in processes, products, and services.
Deming Customer Model:
As per Deming, quality is a product or service that provides value to the customers or stakeholders. To understand, control, and improve the business process, he proposes the following key concepts:
- Process inputs, controls, and outputs are each interdependent.
- Use statistical models to control and guide these inputs.
- Use process feedback to redesign existing systems and make them better.
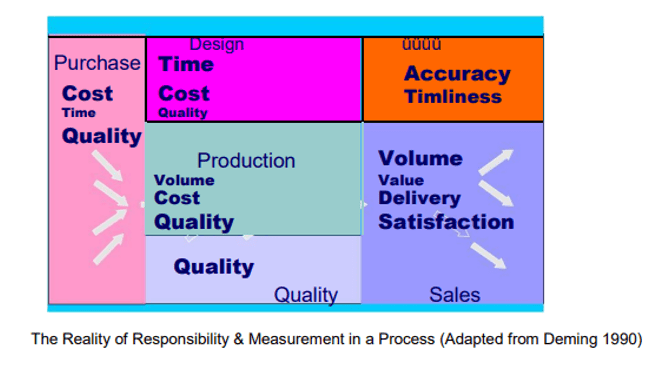
Juran Measures Quality:
Juran has three dimensions for measuring the quality of a process:
- Effectiveness: How well does the output meet the customer’s needs?
- Efficiency: The ability to be effective at the least cost.
- Adaptability: How well you can be effective and efficient in the face of change.
What are Business Processes?
A business process is a collection of interrelated operations that deliver products and services to the customer. Following that logic, the business process can be visualized in a flow map or process matrix. Business processes will help the organization to achieve its objectives accordingly. Thus, Six Sigma plays a vital role in understanding and improving the business process.
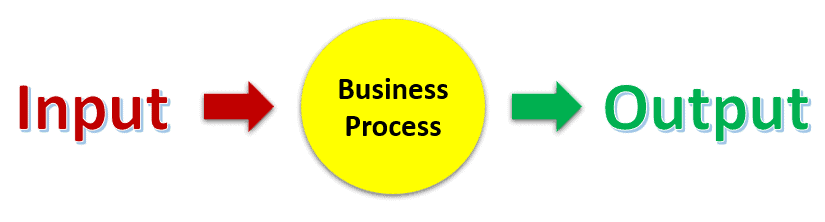
Every activity will have three elements (input, process, and output) that affect its function. Describe the relationship among various business processes (design, production, purchasing, accounting, sales, etc.) and the impact these relationships can have on business systems. A business process is a series of actions, changes, or functions bringing about a result or value to the customers or stakeholders.
Types of Processes
- Operational processes– Operational processes focus on executing the primary tasks of a business. Hence, they are also called “core business processes”. For example, customer service, manufacturing, delivery, etc.
- Management processes– Management processes ensure the operational processes are performing as planned. For example, planning, monitoring, etc.
- Governance processes– These processes ensure the core business is working in full compliance with statutory and regulatory requirements. For example, legal, quality, compliance, etc.
Why Business Process Management?
- A business process is an organizational asset that creates value for the customer.
- Organizations need to measure, monitor, analyze, and control the process to deliver consistent value to the customer.
- The main aim of business process management is to improve revenue and reduce costs.
- Create an efficient work environment.
- Improves quality and enhances customer satisfaction
Tools and Techniques to Enable Business Process Management
SIPOC
The acronym for SIPOC stands for Supplier, Input, Process, Output, and Customer. A SIPOC is a high-level process mapping tool to help visualize a process and its influences. In other words, it is a useful tool that depicts how a process serves the customer and summarizes the inputs and outputs of a process in a visual format.
Process Performance Metrics
We can use many Process Performance Metrics to measure our processes’ current and future value. Once you understand the Process Performance Metrics available and how to use them, then the next step is to decide which metrics are most appropriate.
KPIV, KPOV
Key process input variables (KPIVs) may be analyzed to determine the degree of their effect on the process output variables. It is also known as KPOVs. Hence, KPIV is the prime factor determining the key process output variable (KPOV) or product quality. Furthermore, we use key performance indicators (KPIs) and key process output variables as metrics to tell us how we’re doing.
Stakeholder Analysis
Stakeholder analysis identifies people who have a stake in our product. We use stakeholder analysis before planning a project because we need to know who we need to talk to and what we’ll need from them.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking is an improvement process in which a company measures its current methods and performance, compares them against a standard, and then measures them against world-class performers / best-in-class companies. Once the comparisons are complete, you then combine the best of your process and theirs to create the best possible performance.
Critical to X.
Critical to X requirements are elements of a project that are important to the end customer. Six Sigma projects can aim to improve any of the CTX requirements.
Advantages of Business Process Management
- Easy to monitor and control business processes
- It provides management with an increased ability to identify the bottlenecks
- Increased ability to identify the areas of optimization to improve customer satisfaction
- Helps to reduce the lead times
- Clearly determines the roles and responsibilities of the individuals
Helpful resources
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-introductiontobusiness/chapter/reading-functional-areas-of-business/
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-introbusiness/chapter/functional-areas-of-business-2/
- https://quizlet.com/179044944/introduction-to-business-processes-chapter1-quiz-flash-cards/
- http://www.csun.edu/~dliu/IS551%20PPTs/ERP_01%20-%20Biz%20Functions,%20Processes,%20Data%20and%20Sys%20Dev%20(Edited).pdf
Business Process Management Videos
When you’re ready, there are a few ways I can help:
First, join 30,000+ other Six Sigma professionals by subscribing to my email newsletter. A short read every Monday to start your work week off correctly. Always free.
—
If you’re looking to pass your Six Sigma Green Belt or Black Belt exams, I’d recommend starting with my affordable study guide:
1)→ 🟢Pass Your Six Sigma Green Belt
2)→ ⚫Pass Your Six Sigma Black Belt
You’ve spent so much effort learning Lean Six Sigma. Why leave passing your certification exam up to chance? This comprehensive study guide offers 1,000+ exam-like questions for Green Belts (2,000+ for Black Belts) with full answer walkthroughs, access to instructors, detailed study material, and more.


Comments (2)
When I clicked on KPIV.KPOV, the contents show Balanced Scorecard and Dashboard. Just wondering if the content was correct ?
Hi Mong,
While this page is a bit underconstruction, the link to KPOV is accurate.
Sometimes I’ll group related concepts together into a single resource. If you’ll read the linked article, you’ll see a robust section on KPIs & KPOs.
Best, Ted.