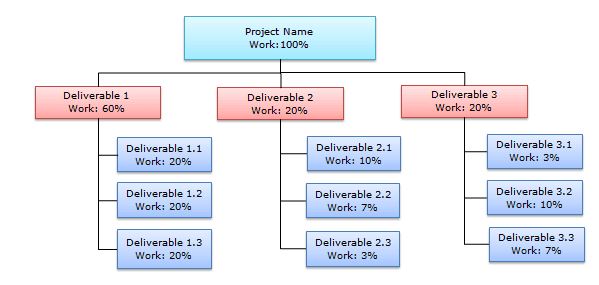
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical representation or decomposition of the work required to complete a project. It breaks down the project into smaller, more manageable components, providing a clear and structured view of the project scope.
The WBS organizes the project’s deliverables, tasks, and sub-tasks in a hierarchical format, starting from the top-level project and breaking down into increasingly detailed levels.
The WBS serves as a foundation for various project management processes, including scope definition, schedule development, budget, resources, and progress tracking.
Why Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A WBS serves as a framework for project planning, scheduling, and resource allocation. It helps project managers and teams understand and visualize tasks, connections, and dependencies.
Furthermore, by breaking down the project into smaller elements. It becomes easier to estimate, assign, and track the progress of tasks, as well as manage project risks and costs. WBS is a foundation document in project management because it provides the basis for planning and managing project schedules, costs, and resources.
History of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The concept of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) has been in use in project management for several decades, and it is difficult to attribute its invention to a single individual.
Many credits the formalization of the WBS as a project management tool to the United States. Department of Defense (DoD) and the establishment of the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) in the late 1950s. The DoD recognized the importance of breaking down work into manageable elements for complex projects and introduced the concept of the WBS as part of their project management practices.
WBS Basic Principles
- The work content of a WBS item is the sum of the WBS items below it
- A WBS item is the responsibility of only one individual, even though many people working on it
- The WBS must be in-line with the way in which the work is actually going to be performed
- All the project team members should be involved in developing the WBS to ensure consistency
- The WBS must be a flexible tool to accommodate inevitable changes while properly maintaining control of the work content in the project according to the scope statement.
How to create a WBS
- Define the project and goals: The first step of WBS is to define the structure of the project. The project charter serves as the documentation for the project scope, team members, goals, and objectives.
- Determine the project boundaries: The WBS should include clear delineations of the project boundaries.
- List the project deliverables: Provide a complete list of all project deliverables required to complete the project.
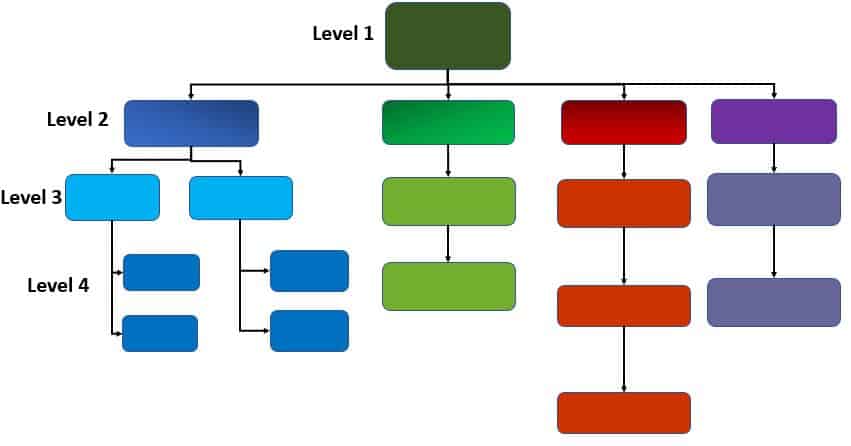
- Define Level1 elements: Level 1 elements are summary deliverables that should cover the total project scope
- Decompose (breakdown) level 1 elements: Break down level 1 elements into smaller and smaller pieces. The process of breaking down level 1 elements is called decomposition.
- Create Gantt charts for the WBS: Export or enter the Work Breakdown Structure into a Gantt chart for further scheduling and project tracking.
Why would you use it?
Project managers utilize a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for multiple purposes in project management.
- Scope Definition: The WBS helps to define and clarify the project scope by breaking down the work into smaller, manageable components.
- Planning and Scheduling: The WBS provides a framework for project planning and scheduling. It allows project managers to assign resources, estimate time, and create a plan to execute individual tasks and the entire project.
- Task Assignment and Responsibility: The WBS helps in assigning tasks and responsibilities to team members.
- Resource Allocation: The WBS assists in resource allocation by identifying the resources needed for each task or sub-task.
- Cost Estimation and Budgeting: The WBS enables accurate cost estimation and budgeting.
- Progress Tracking: The WBS allows for effective progress tracking and monitoring of each task and sub-tasks.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement: The WBS provides a structured and visual representation of the project. It is making it easier to communicate project details and progress to stakeholders.
- Risk Management: The WBS helps identify and manage project risks by breaking down the project into smaller sections. This allows for a proper analysis of potential risks and enables the implementation of effective risk mitigation plans.
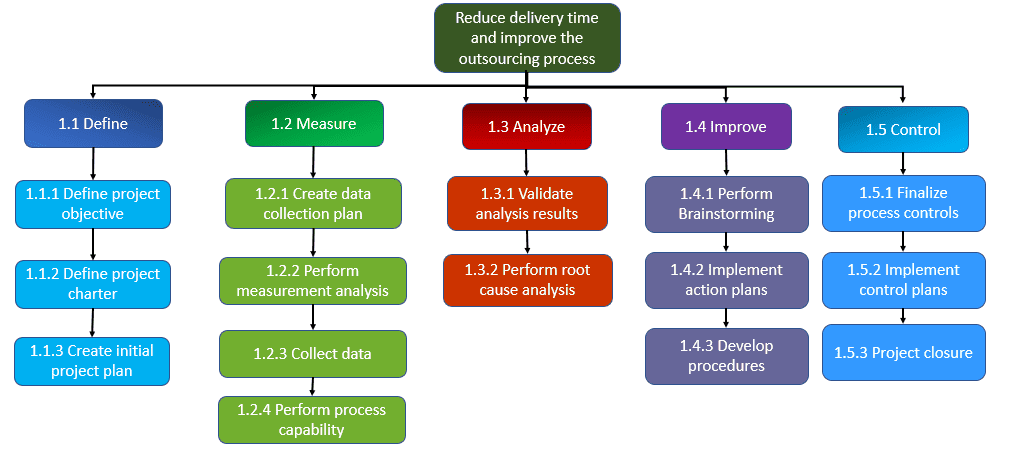
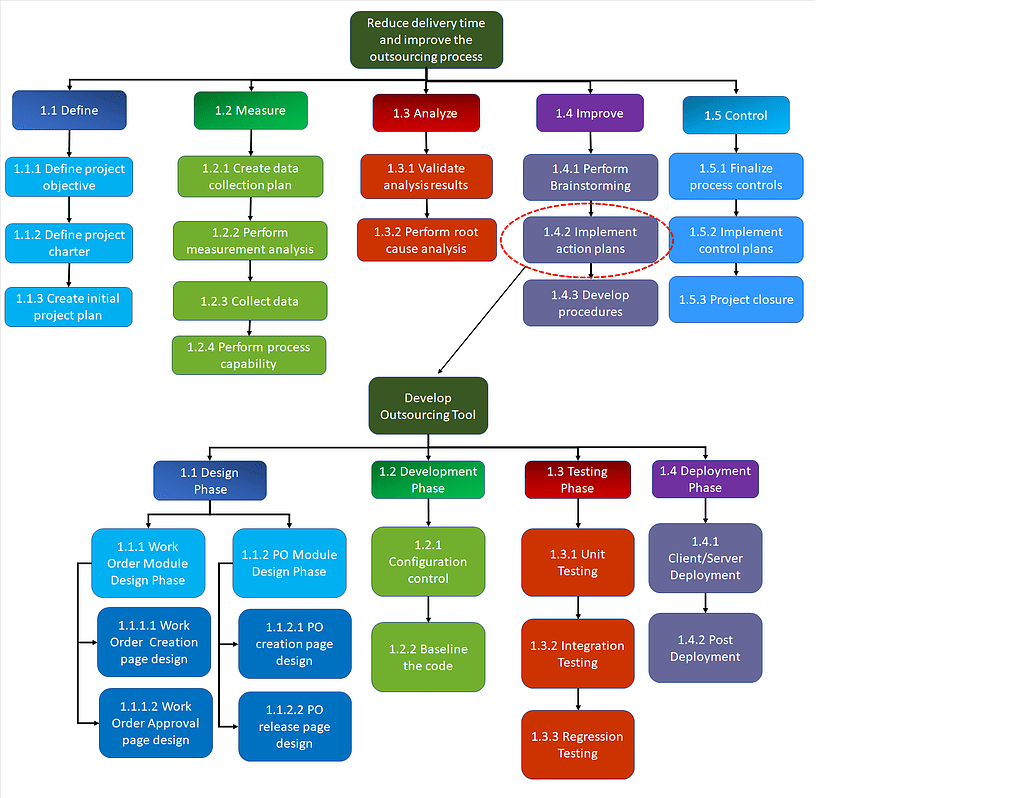
Six Sigma Example
Example: A leading aerospace company utilized the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to enhance delivery commitments. The objective was to reduce delivery time and improve the outsourcing process (the time that the IT application is not available for users). This, in turn, would increase return on investment (ROI) and user satisfaction. The following is the WBS to execute and deliver the project.
Benefits
WBS is a valuable tool for project planning, organization, and control. Following are the key benefits of WBS
- Clear project organization and structure.
- Precise definition and control of project scope.
- Efficient resource allocation and scheduling.
- Enhanced communication and stakeholder engagement.
- Effective risk identification and management.
- Accurate cost estimation and budgeting.

