Team Dynamics, Mechanics & Communications is divided into what teams do (meetings, process) and how they do it (decision making).
Team dynamics is the force that inspires or drives a group of people to work collectively for a common cause or objective. A good team is a team with different personalities and also a common identity.
Team mechanics refers to conducting meetings with proper agendas, times, and locations and distributing the meeting minutes to all stakeholders. In fact, meetings are an essential part of sharing information and making decisions that help to capitalize on the strengths and experiences of a group of people with common goals.
Team communication is the foundation of team collaboration. A communication process will complete only when feedback is received. Ex: When a task is assigned, the worker acknowledges the responsibility and describes how he will perform the task.

Effective communication
Effective internal and external communication is one of the crucial aspects of organizational success; otherwise, improper communication will lead to failure. Strong team communication skills can help build relationships, ensure the sharing of new ideas and best practices, and benefit team members through coaching and counseling.
Furthermore, team communication skills are critical for ensuring the success of the team effort. But communication barriers influence the communications loop. Barriers include:
- Personal bias
- Non-assertive behavior
- Anger or frustration
- Lack of confidence
- Inappropriate priorities
- Distractions
- Interruptions
- Rank differences.
Steps for effective communication amongst the team include:
- Use standard terminology when communicating information.
- Request and provide clarification when needed.
- Use nonverbal communication appropriately.
- Use proper order when communicating information.
- Repeat, as necessary, to ensure communication is accurately received.
- Inform the appropriate individuals when the mission or plans change.
Vertical communication vs. Horizontal communication
Horizontal communication is the information transmission between persons with the same position level in an organization. Particularly, it helps to share ideas, suggestions, and attitudes between peers and colleagues. It may also increase job satisfaction and motivation by creating more employee empowerment in communication.
Vertical communication, on the other hand, is when information flows systematically between supervisors and subordinates (up and down). It helps management to stay in control of the organization.
Team Communication Videos
Team Dynamics, Mechanics & Communications during Meetings
At its best, a team meeting is a way to ensure the staff and management teams are aligned. Team meetings should be reviewed regarding processes, results, and relationships. However, team meeting needs a logical structure for many reasons, including time management.
Following are the guidelines for productive team meetings:
- Create meeting agenda and circulate it to stakeholders in advance.
- Start the meeting on time and also record the minutes of the meeting.
- Arrange visual aids (like flip charts etc.).
- Review previous meeting action items status and also move unfinished items to the next meeting.
- Monitor team participation, conflict resolution, and problem-solving process.
- Summarize points and also assign responsible persons for each action item.
- Finish the meeting on time and, finally, circulate the meeting minutes to all the attendees.
Team Dynamics, Mechanics & Communications for Decision Making
No organization can consistently succeed in any market without quality decision-making. Teams are particularly effective in problem-solving if they comprise people with complementary skills. Below are the different types of decision-making.
Types of decision making
- Authoritarian: Authoritarian is one of the decision-making methods where typically authority lies with one person who makes decisions very quickly without considering inputs from others.
- If the authority lies with the right person, the organization benefits from the right decision. However, it has many disadvantages, as decision-making lacks the involvement of stakeholders affected by the decision. Hence, it should not use in Lean Six Sigma projects.
- Consultative: This is one of the decision-making methods where one person holds the decision-making authority but will take input from all the affected parties. Consultative decision-makers seek input from the team before deciding, for example, polling the group to see if we should continue with a meeting if a team member is sick.
- Consensus: Consensus is one type of decision-making method where all the stakeholders/parties provide input for decision-making, and the team will not destroy the final agreed decision. Achieving consensus is the preferred method of decision-making in a Lean Six Sigma team, and also this is the most effective decision-making method in Six Sigma.
- Voting: In most cases, the consensus is not a viable solution. In such scenarios, the team may opt for the voting method. Teams will finalize the decision if two-thirds (majority) agree on it. However, the disadvantage of this method is clashes between two parties (the losers and the winners). This method is rarely used in Lean Six Sigma projects.
- 100% agreement: 100 % agreement is the rarest of the rare decision-making option, especially in lean Six Sigma projects involving diverse stakeholders.
Decision-Making Techniques
- Brainstorming: Brainstorming is the basic technique for getting people to gather a list of ideas spontaneously and solutions.
- A cause-effect diagram can use brainstorming points as input.
- Negative Polling:
- “Is there anyone who disagrees with these ground rules?” Very quick.
- A negative poll is conducted when the meeting facilitator asks a question such as, “Does anyone disagree with the ideas we just discussed?” If everyone is silent, the team will know everyone agrees, and they can move on to a new issue without wasting much time.
- A technique used to establish team agreement without taking a lot of time.
- Multivoting: Multivoting is a way for a group to narrow a list of choices down to a manageable few.
- Nominal group technique: The nominal group technique is a variation of brainstorming where individuals develop ideas independently rather than as a group.
- Force Field Analysis: Force Field Analysis is a method for listing and evaluating the forces for and against a situation.
Team Dynamics, Mechanics & Communications for Facilitation
Ground rules should be established as a preventive measure to avoid misconduct, not as a reactive measure. In addition, the team leader must understand group dynamics. Facilitators help assist a group in the following ways.
- Conduct skill gap analysis and identify team members that need training
- Avoiding team bottlenecks
- Clarifying points of view on issues
- Collate and summarize points made by the team
- Provide feedback on team effectiveness
- Focus on progress
- Assess the change process
- Keeping the team on track with the process
- Coach the leader and participants too
The team facilitator must avoid
- Dominating the group discussions
- Solving a problem or giving an answer
- Being judgmental of team members or their ideas, opinions
- Taking sides or becoming caught up in the subject matter
- Making suggestions on the task instead of on the process
Team Training
Training Needs Assessment
Training needs assessment is a crucial first step in the team training process. Moreover, it helps to identify the gap between adequate and inadequate performance.
The organization has to collect information regarding key company needs and investigate the possible performance gap. Subsequently, the organization has to analyze the assessment data and plan the training requirements for each level (organization, process, and job levels).
Training Resources
The main objective of the training is to improve the skills and knowledge of individuals. Training material is one of the essential training resources and should be presented at the appropriate level to the target audience. The following are the different resources required for an effective training program.
- Good training material
- Proper lighting of the training room
- Temperature and ventilation
- Ling of sight
- Accommodations
- Furniture
Training Tools
Classical training tools: Classical training is usually conducted in the presence of an instructor or self-study by individuals. Lectures, tutoring, case studies, seminars, speeches, workshops, homework, demonstration, student presentations, and on-the-job training are the different classical training tools.

Advantages of classical training tools
- Low cost for preparation of training material
- Quick adjustment to the training material based on class needs
- Additionally, an instructor can clarify students’ questions immediately
Disadvantages of classical training tools
- High training cost per individual
- High efforts to coordinate the participant schedules
- The number of qualified instructors may be limited
Technological training tools: Technology-driven methods like online videos, training tapes, etc. For the most part, growing demand is placed on individuals for flexible training schedules, locations, and amount of training sessions.

Advantages of technological training tools
- Training material can be repeated by the user, particularly if not understood.
- An individual can control the training session.
- Multiple individuals can run the same training session in different geographic locations.
Disadvantages of classical training tools
- High initial training cost for preparation of training material
- Difficult to modify the content based on class need
- The student learning curve is longer
Adult Learning
Adult learners are typical students in the manufacturing sector. Adults are self-directed and responsible and do not need to be controlled in their learning experience. Below are the key characteristics of adult education.
- The trainer must consider the various constraints while planning a training session for adults as they have more life responsibilities.
- Adults’ motivation is high to learn.
- Adult’s learning curve is different than young people’s.
- Lack of self-confidence as they have been away from the classroom for a long period of time.
Training Program Evaluation
Collect the feedback soon after the completion of the training. In fact, this will enable the evaluation of the instructor’s knowledge, training content, training material, training environment, and the total value of the training.
The key measure of the training program’s effectiveness is whether its benefits exceed the costs. The team needs to apply the concepts on a small scale and also needs to use the concepts as earliest. Otherwise, there is a possibility of forgetting the concepts.
Team Dynamics, Mechanics & Communications for Motivation
Motivation is the art of getting people to do what they suppose to do, and surely, it is one of the key elements of a manager’s responsibility to motivate their people. Indeed, it is the most challenging responsibility for management to sustain and increase team motivation.
Below are a few modern motivational theories:
Abraham Maslow
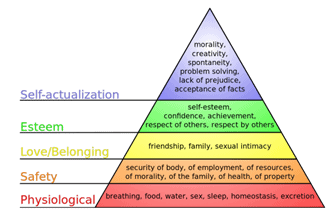
According to Maslow’s “A Theory of Human Motivation,” an individual’s most basic needs (bottom of the pyramid, like breathing, water, food, etc.) must be met and relatively satisfied, and higher-order needs must be met to sustain satisfaction.
- Self-actualization needs: Morality, creativity, problem-solving
- Esteem needs: Confidence, Respect, achievement, recognition
- Love/Belonging (Social) needs: Love, friendship, relationships
- Safety needs: Protection, security, and stability
- Physiological needs: Basic human needs; air, food, water, housing
Alderfer’s ERG
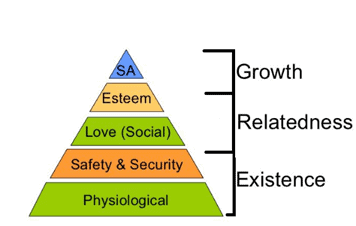
Similar to Maslow’s hierarchy, it focuses on differing levels of needs, which are usually satisfied in order of importance. Unlike Maslow’s theory, it allows for higher needs to be met before lower-level needs under certain circumstances.
- Existence Needs: Existence needs are related to the basic survival of human beings. However, they are similar to the physiological and safety needs suggested by Maslow. For example, Monetary rewards, working conditions, job security, and incentives are some examples of existence needs.
- Related Needs: The individual has a natural desire to develop social relationships. These needs are related. These needs are similar to social and esteem needs to be enunciated by Maslow.
- Growth Needs: Individuals intrinsically desire to grow in their organizational career and personal life. These are growth needs. Moreover, they are similar to the self-actualization needs suggested by Maslow.
Frederick W. Herzberg
Frederick W. Herzberg’s theory, also called the Motivation-Hygiene theory or the dual-factor theory, was penned by Frederick Herzberg in 1959. He developed the theory that people’s job satisfaction depends on two kinds of factors. Factors for satisfaction (motivators/satisfiers) and factors for dissatisfaction (hygiene factors/ dis-satisfiers) are referred to by a variety of names, such as
- Dis-satisfiers and Satisfiers
- Maintenance factors and Motivators
- Hygiene factors and Motivators
- Extrinsic factors and Intrinsic factors
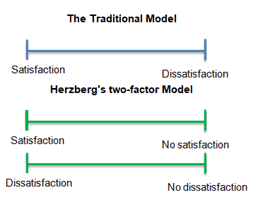
Motivating factors have uplifting effects on attitude or performance. Hygienic (or maintenance) factors prevent loss of morale or effectiveness.
Team Dynamics, Mechanics & Communications for Conflict Resolution
Conflict is the outcome of mutually exclusive views evident by emotional responses such as anger, fear, and frustration. Obviously, some conflicts are unavoidable in human relations. The following are the common source of conflicts in an organization.
- Organizational hierarchy
- Job pressure
- Change in organization procedures
- Different objectives and goals
- Changes in priorities
- Team clashes
The following guidelines help the team leader to resolve conflicts.
- Decide how important the issue is to resolve
- Determine the stakeholders involved in the conflicts
- Conduct private meeting
- Ensure all the stakeholders understand the responsibilities
- Enforce all parties toward problem definition
- Motivate the team to propose a solution
- Evaluate the cost of each solution and identify the best solution
- Collect feedback from participants to improve the process further
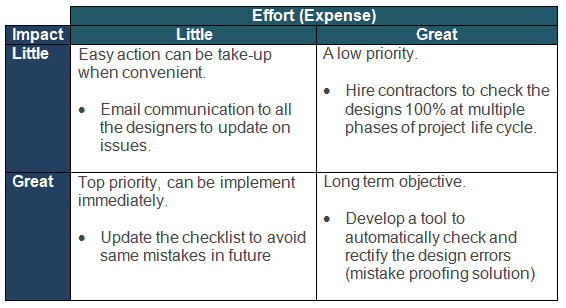
Add Effort / Impact model
One of the feasible methods to select the appropriate action item is to identify and compare the impact of the action with the effort (or expenses) to achieve it. The only disadvantage of this method is getting objective evidence of the data to fill the matrix, as most of the time, parties subjectively agree on the appropriate classification.
Example: ABC Inc is a design support supplier for an automobile company. The customer identified mistakes in the drawings submitted by ABC. The team leader opted for the effort/impact method for resolving conflicts and making decisions.


Comments (2)
Hi Ted, one of the quiz questions/answers state that Multi-Voting is NOT a decision making tool but, it is listed above as a decision making technique. Is there a difference between tool and technique?
Hi Matt,
Happy to help! Let’s discuss this in the member’s area. Can you make a forum post and include the question text?
Best, Ted.