What are Customers?
Customer identification is a crucial step of Voice Of Customer (VOC) process. A customer is a person or company that purchases products or services. Customers are the most important part of a Six Sigma project. Six Sigma is entirely built around the concept of a customer. Customers define quality and thus the expectations (ex: Quality, delivery, service, technical skills, etc.) for how processes perform.
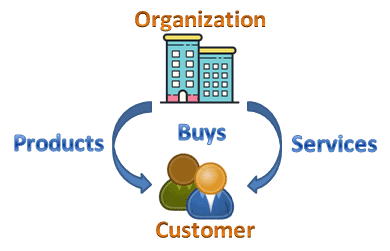
Customers can be broadly categorized as:
- Business to customer (B2C), for example, where a person buys groceries from a store.
- Business to business (B2B), for example, a hardware shop uses the service of an accounting firm for tax returns.
- Customer to business (C2B), for example, where an individual sells his vegetables to a store.
- Customer to customer (C2C) is where customer sells goods to each other, for example, in an online e-commerce portal, one consumer sells his product to other consumers.
Identifying and Reaching out to Customers
Six Sigma details the ways to identify the key customer categories for the business. It is a crucial step of the VOC process as the end user can easily tailor products and services accordingly and thus helps the company to become a customer-focused company and acquire customers easily whilst retaining existing customers.
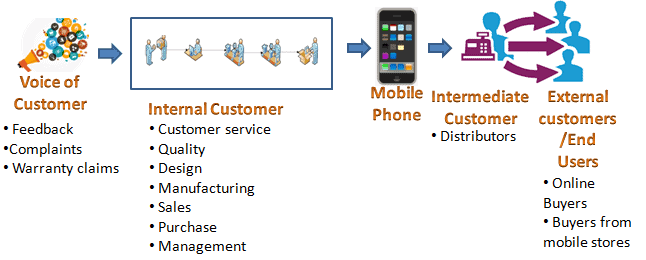
The organization captures the needs and expectations of the customer i.e., the voice of customer (VOC). The organization’s process includes various steps to convert inputs to output (product or service) to be delivered to the customers.
Identifying and understanding customer requirements is essential so the products or services can be designed accordingly.
Customers may be classified as internal customers and external customers
Internal Customers
An internal customer is anyone within the business system who is affected by the product or the service while it is being developed. The internal customer is usually an employee of an organization and is forgotten as management focuses more on the external customer. Production, marketing, sales, design, sales, maintenance, and planning departments should think of themselves as service providers.
Internal customer activities affect the system’s next process and the quality of the end product. Much research shows that employee engagement activities within the organization have a direct impact on customer satisfaction. When employees are motivated and provided with the proper tools, resources, and innovation culture, they will be happy to go the extra mile to satisfy the customer.
Internal communication for customer satisfaction can be improved in the following ways:
- Periodic newsletters consisting of basic business information and corporate
- Display project updates, memos, etc
- Discuss project issues and new business opportunities in team meetings
- Celebrate innovation or quality awards received from customers
- Communicate goals, customer feedback, etc.,
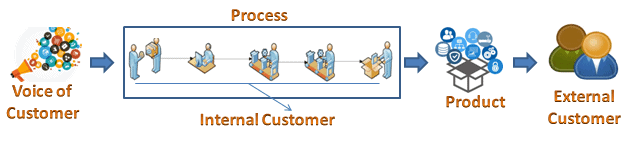
External customer
External customers are not employees of the company but are impacted by it and usually consist of end users and intermediate customers. Customers may define or sets the requirements of the product or service; they may be external customers, end users, regulatory agencies, governments, etc. An external customer provides a major part of company revenues.
Organizations will need to understand the needs and expectations of external customers to design their products and services well. Customers will weigh the value of a product based on the cost, quality, availability, and features. Hence, it is important to know the Voice Of Customer (VOC). The following are the different methods to collect customer information.
- Customer surveys
- Focus group
- Customer complaints
- Face-to-face interviews
- Scorecard
- Market research
Organizations must review the information gathered from the Voice Of Customer (VOC) and identify the customer needs and new trends in the market. The trends will help organizations develop innovative solutions to retain customers. Customers seem to be more satisfied when suppliers collect feedback and implement the changes suggested by them rather than not receiving the feedback request from the supplier.
Intermediate customers:
Intermediate customers purchase the product or service from an organization and then modify, repackage, re-assemble, and sell those products or services to end users. Ex: Wholesalers, distributors, agents, etc.
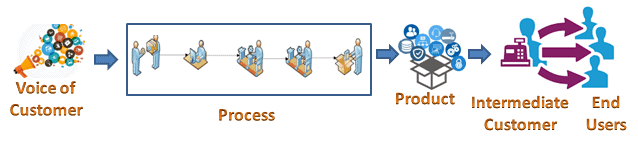
End Users:
One of the categories of external customers, who buy the product or seek the service for their own purpose, is the actual end user of the product example: people who buy a mobile phone from the store, or a guest in the hotel.
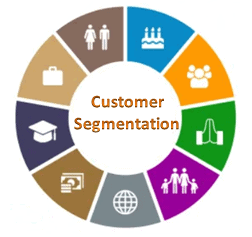
How to Segment Customers
Customer segmentation provides insight into the landscape of the market, revealing customer characteristics that can be used to group customers into segments that have something in common this process is also known as clustering. Customers are also categorized on basis of demography (like age groups and geographical location) and industry types as well. Typical segmentation includes
- Geography – region, county size, city
- Demographic – age, sex, family size, income, occupation, race
- Buyer behavior – heavy user, aware of the need, status, loyalty
- Volume – grouping based on usage of the product (heavy, medium, light)
- Marketing factor – brand loyal customers
- Product space – customer perception comparison
You can divide external customers into business customers or consumer customers. Business customers can include for-profit and not-for-profit companies. The consumer customer consists of a large number of customers with small purchases, as against business customers.
Customer Retention
Customer Retention refers to the activities and actions organizations take to reduce the number of detections. Successful customer retention efforts indicate how an organization or brand understands and meets customer needs.
Customer retention reflects customers’ mindset about an organization and its products or services when their expectations have been met or exceeded. This state reflects the lifetime of the product or service experience.
While most organizations traditionally spend more money on acquisition because they view it as a quick and effective way to increase revenue, customer retention is seven times more cost-effective than landing new customers.
The benefits of customer retention are as follows:
- Reduces acquisition cost
- Increases client base
- Increases turnover
- Makes relationships profitable
- Creates more word-of-mouth publicity
Customer Service
Customer service is the act of taking care of the needs of the customer by providing and delivering professional, high-quality service and assistance before, during, and after the purchase of a product or service.
Top management periodically monitors the customer service activities in the organization, and they need to listen to the customer, provide training, monitor the response metrics, and communicate the improvement activities in the area of customer service.

The advantages of customer service are as follows:
- Existing customers are more likely to buy based on the services provided by the organization
- Improves customer retention
- Great customer service results in a lower number of complaints
- Improves the company brand value
- Improves the employee turnover
- Opens the opportunity for new business or partnerships
Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty indicates the extent to which customers engage with a company’s products or services and how strongly they tend to select one brand over the competition.
Loyal customers are arguably the most important factor in achieving business success. Success from customer loyalty creates repeat business and more opportunities. The major strategies for increasing customer loyalty are keeping it personal and always following up.
Loyal customers spend more than new customers as they know very well about the product and service, and also they will refer to others and recommends the product and service. As per the research, 40% of US online shopping revenue comes from repeat loyal customers, who generally make up just 8% of site visitors.
Six Sigma Project Impact on Customers
Example: ABC Manufacturing Company sells mobile phones online and via distributors. The customer service department tracks the number of customer complaints received from the distributors and also online customers on monthly basis. Hence, the General Managers of the plant asked Quality Managers to initiate the Six Sigma project to reduce customer complaints and warranty claims which are 10% of the revenue.
Following are the impacts on various stakeholders in the value chain
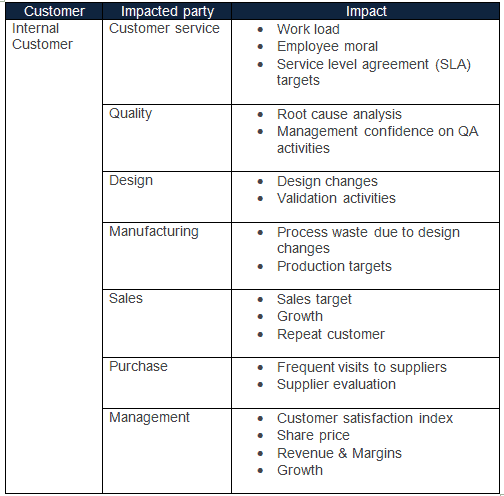
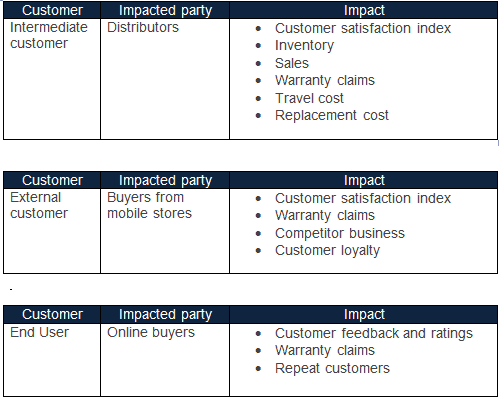
An effective Six Sigma project improves internal customer satisfaction (generally the employees of an organization), reduces process waste, designs changes, and improves business growth and sales. It will also improve external customer and end-user satisfaction, increase repeat customers, and also customer loyalty. Furthermore, it will improve the sales and growth of an organization.
Helpful Articles for Customer Identification
- https://videos.asq.org/asq-tv-ep-1-the-customer-experience
- https://videos.asq.org/asq-tv-ep-1-the-customer-experience
- Client/Customer/End User/Internal customer

